Respiration Definition
“Respiration is defined as a metabolic process wherein, the living cells of an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP) by taking in oxygen and liberating carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances.”
What is Respiration?
Respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in all organisms. It is a biochemical process that occurs within the cells of organisms. In this process, the energy (ATP-Adenosine triphosphate) is produced by the breakdown of glucose which is further used by cells to perform various functions. Every living species, from a single-celled organism to a dominant multicellular organism performs respiration.
Let us have a detailed look at the different types of respiration in organisms.
Types of Respiration
There are two types of respiration:
Aerobic respiration
It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. It is a continuous process that takes place within the cells of animals and plants. This process can be explained with the help of the chemical equation:
Anaerobic respiration
It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen to produce energy. The chemical equation for anaerobic respiration is
Phases of Respiration in Organisms
Respiration occurs in the cytosol and around the plasma membrane in prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, respiration takes place in the mitochondria, which is also considered the powerhouse of the cells.
This process is very much similar to the internal combustion of the car engine, wherein organic compounds and oxygen go in, while water and carbon dioxide comes out. The energy that is liberated powers the automotive (or cell).
The three phases of Respiration are:
Glycolysis
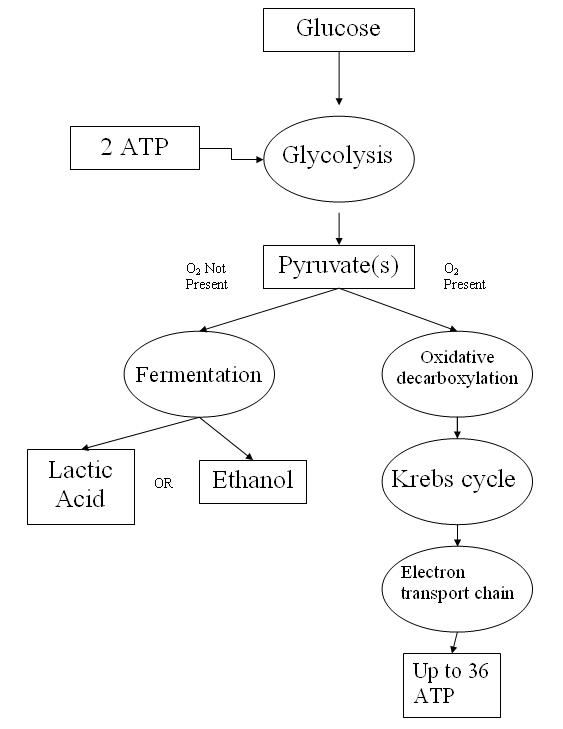
The molecules of glucose get converted into pyruvic acid which is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, leaving two carbon molecules, known as acetyl-CoA. During the process of glycolysis, two molecules of ATP and NADH are produced. Pyruvate enters the inner matrix of mitochondria and undergoes oxidation in Kreb’s cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
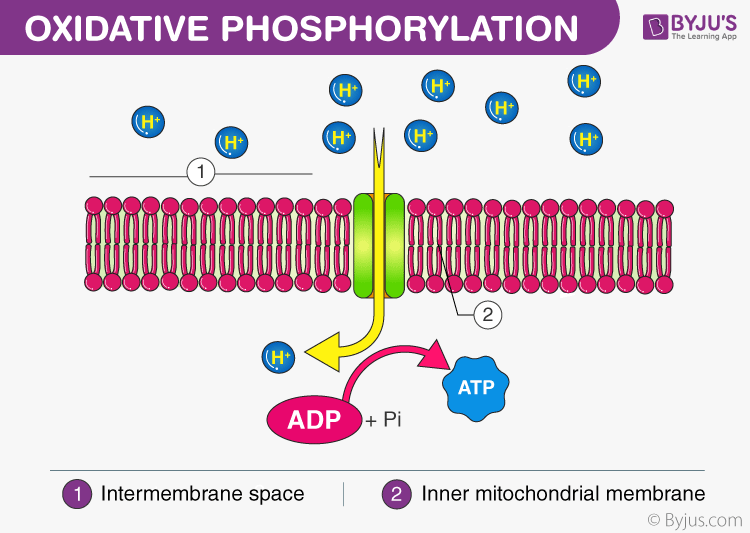
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP molecules are formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of electron carriers. This process takes place within the mitochondria of a cell.
Citric Acid Cycle
This is also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle or Kreb’s cycle. Two ATP molecules are produced in each phase of the citric acid cycle and it takes place within the mitochondrial matrix of a cell. The electrons generated in Kreb’s cycle move across the mitochondrial matrix.
No comments:
Post a Comment